Conductor Resistance Evaluation
- Test summary/features
-
PCB through-holes and solder junction cracks can cause wire breaks and contact failures greatly affecting the reliability of electronic devices. Crack formation causes include internal factors such as the connection method, solder material and flux activating agent type/cleaning method, as well as external factors such as temperature and humidity. Conductor resistance evaluation is a test method that detects crack formation or contact failure from conductor resistance changes when temperature and humidity (external factors) are varied.
- Test equipment
- ESPEC's conductor resistance evaluation systems (AMR) are connected to thermal shock test chambers and a temperature and humidity chamber to detect crack formation by detecting changes in conductor resistance in real time, enabling evaluation testing of contacting parts such as PCB through-holes and solder junctions, and connectors and switch relays.
- Equipment particulars
-
- Conductor Resistance Evaluation System (installed at Kobe, Utsunomiya and Toyota Test Centers)
-
- Features
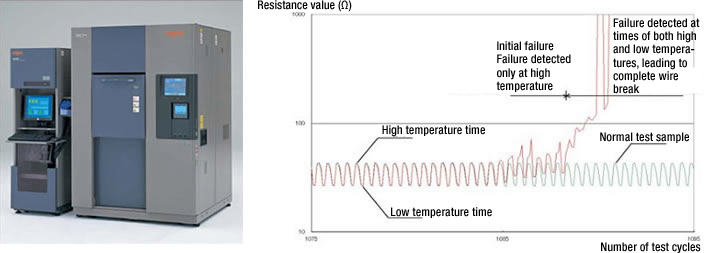
- To detect cracks, a conductor resistance (connection resistance) is placed in a temperature cycle environment and measured continuously. This type of test was previously handled by stopping the test after every fixed test cycle and measuring the conductor resistance (connection resistance) of the solder connections at ambient temperature. But test sample contraction often prevented connectivity problems from being detected with ambient-temperature measurement even when cracks had formed, resulting in failure detection variation.
Using an automatic conductor resistance evaluation system (AMR) for measurement enables resistance to be measured at low and high test temperatures, enabling reliable crack detection. Crack formation can be monitored during all test cycles, enabling precise identification of the cycles in which failures occur.
- Cross-section observation photo
-

About 1,750 cycles
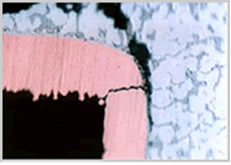
About 1,800 cycles
- Measurement system applications
-
In addition to solder connection evaluations, AMR systems are used for testing done for development/evaluation of various connection methods.
- Connection evaluations of conductive adhesives and anisotropic conductive films
- Contact resistance evaluations of connectors and other parts making contact
- Contact resistance evaluations of switches, relays and similar components
- Connection evaluations of different metals
